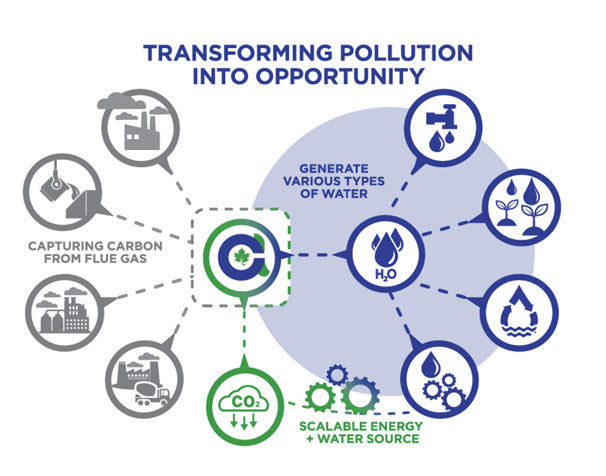
Our patent-pending technology can also generate water from Flue Gas (Exhaust Gas, Vent Gas, Stack Gas) while it captures carbon. The generated water could be provided in following categories:
We use a portion of the water we generate from Flue Gas (Exhaust Gas, Vent Gas, Stack Gas) to capture CO2. The extracted CO2 could be used for:

The use of water by industries represents a significant portion of total water use. U.S. industrial water use is estimated to be more than 18.2 billion gallons per day. While industrial water withdrawals account for just five percent of total water withdrawals in the United States, thermoelectric power water withdrawals account for 49 percent. Industrial and manufacturing businesses also use about 12 percent of the public water supply. Industrial water users include facilities involved in sectors such as chemicals, food and beverage, paper and associated products, steel, electronics and computers, metal finishing, petroleum refining, and transportation equipment.
Water scarcity is one of the main consequences of global warming and water dependent industrial facilities are already under regulatory and public pressure to find alternative water sources instead of depleting precious local community fresh water supplies.
Generating water from the facility exhaust gas can help the facility owners to meet the carbon emissions requirements and improve their resiliency against financial, social and environmental water supply challenges.
Ultrapure water (UPW) is used in a number of industries, each with its challenges. The primary industries using Ultrapure Water (UPW) are:
The semiconductor industry has recently dominated international media attention as it faces an unprecedented water shortage that makes production challenging. How can these industries source enough ultrapure water to continue operations when long-term climate projections call for increasingly arid conditions?
Our on-site water production from Flue Gas (Exhaust Gas, Vent Gas, Stack Gas) can play an important role in the future of UPW dependent industries by offering a low carbon local source for the industry.

Managing water sustainably is key to the future of food and agriculture. Agriculture production is highly dependent on water and increasingly subject to water risks. It is also the largest using sector and a major polluter of water.
Agriculture is expected to face increasing water risks in the future. In recent years, agricultural regions around the globe have been subject to extensive and increasing water constraints. Major droughts have affected agricultural production while diminishing surface and groundwater reserves. Climate change is projected to increase the fluctuations in precipitation and surface water supplies, reducing snowpacks and glaciers and affecting crop’s water requirements. Coupled with these changes, farmers in many regions will face increasing competition from non-agricultural users due to rising urban population density and water demands from the energy and industry sectors.
Utilizing industrial exhaust gas to generate water can help with both water scarcity and carbon emissions issues. Our technology can also be used for controlling the humidity level within greenhouses and avoid energy losses.

There is the same amount of freshwater on earth as there always has been, but the population has exploded, leaving the world’s water resources in crisis. Climate change is already affecting water access for people around the world, causing more severe droughts and floods. Increasing global temperatures are one of the main contributors to this problem. Climate change impacts the water cycle by influencing when, where, and how much precipitation falls. It also leads to more severe weather events over time. Increasing global temperatures cause water to evaporate in larger amounts, which will lead to higher levels of atmospheric water vapor and more frequent, heavy, and intense rains in the coming years.
One way to reduce treated water demand is to substitute an alternate water supply for an existing demand that does not need treated drinking water. Alternative water is water supplied by sustainable sources that can be used to help offset the use of fresh surface water and groundwater (such as lakes and aquifers).
Our atmospheric water generation system and exhaust gas water recovery technology can make a significant difference in global efforts to sustainably supplement conventional treated water sources.